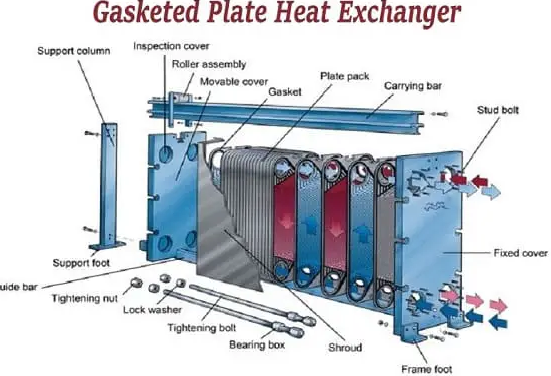
GASKETED PLATE HEAT EXCHANGERS

A plate heat exchanger is a type of heat exchanger that contains a series of corrosion-resistant metal (such as stainless steel, or titanium) to transmit heat between two fluids. The plate heat exchanger works on the principle of thermodynamics. In these heat exchangers, each plate has a confined, hollow tubular shell.
The plates are arranged in such a way that thin rectangular channels are developed to exchange heat through half pieces. The operating fluid moves between these twisted and narrow channels.
The plates of this exchanger are surrounded by gaskets to control the fluid flow. These gaskets arrange in such a way that only one type of liquid (such as oil which is being heated) distributes on one plate and another fluid (such as hot water) distributes on the next plate.
After this arrangement, the cold and hot fluids alternately pass through the plate, whereby a heat exchange takes place. The plates have a large surface area; therefore, they offer an excellent heat transfer rate than tubular heat exchangers. Additionally, our gasketed plate heat exchangers come with a maintenance-friendly assembly and sealing technology, ensuring low service and maintenance costs.